Data collection has become a crucial resource for brands, offering a powerful lever for personalising experiences and optimising campaigns. This guide will help you to understand the challenges of data, even without technical expertise, and to use it to boost your company’s performance.
6 reasons for data collection
Brands can’t navigate by sight. To make the right decisions and above all refine their strategy to remain competitive, they need to understand who they are talking to and what their audience wants. The data enables them to refine their customer knowledge and gain better visibility of their operations.
So why collect data at all?
1. Getting to know your customers better
Data enables brands to identify the expectations, behaviours and preferences of their customers. By understanding their buying habits, interests and online journeys, they can refine their strategies and improve their offering.
Example: A retailer can analyse its customers’ purchasing history to identify their favourite styles. Based on these insights, it can send them recommendations. This is what Legrand did with its campaign for the Céliane brand. Thanks to the interactive mechanism Swiper, Legrand was able to collect more than 115,000 customer preferences.


2. Optimising your marketing campaigns
Using the customer data collected, a brand can precisely target its customers and optimise the ROI of its campaigns. By analysing behaviour, the right messages can be delivered to the right people, at the right time and in the right place.
Example: By tracking the pages visited and the products added to the shopping basket on its site, the retailer can better retarget each of its visitors with personalised advertising.
3. Improving the customer experience
A brand that makes good use of its data can offer a smooth, intuitive and enjoyable shopping experience. Thanks to the data collected on its e-commerce site or its application, it can identify friction points in the customer journey and adjust its experience (by simplifying the checkout process).
Example: An e-commerce company can analyse customer reviews to understand the main frustrations. In response, it can set up a chatbot capable of providing answers to the most frequently asked questions and thus improve its product sheets by including more details.
4. Customise offers and promotions
Rather than sending the same promotions to their customers, brands can use data to propose personalised offers based on consumers’ habits and preferences. These incentives increase loyalty and encourage customers to return.
Example: A supermarket chain can analyse its customers’ regular purchases and offer them targeted discounts on their favourite products. These incentives encourage loyalty and strengthen attachment to the brand.
5. Anticipating demand and managing stocks
Good stock management is essential to avoid stock-outs and limit unsold goods. Thanks to the data it collects, a brand can predict trends and adjust its production/supply.
Example: It is in a brand’s interest to analyse buying trends in order to estimate demand for its models. Using this information, it can adjust its production to avoid stock-outs on models while limiting overstocking on less popular items.
6. Create new products or services
Insights gained from customer data can be used to identify new needs and adapt the existing offering. This can lead to the improvement of a product or the launch of a service to meet the expectations of its audience.
Example: A beauty brand can use the Customizer mechanism to sound out the desires of its community and offer them products that meet their needs.
What are the different types of customer data?
Data is essential information to the management and profitability of a business. The good news is that
there’s no shortage of customer data. A survey revealed that the organisations surveyed manage an average of 3 petabytes (PB) of data, and that this volume doubles every two years.
To avoid being overwhelmed by data, it’s important to focus on the data that can make the difference to your company’s development.
1. The different types of data according to their content
We can start by differentiating customer data according to its content and the information it reveals. Here are the 6 types of data that are useful for brands:
- Demographic data, i.e. information that characterises each user, such as their age, gender, place of residence, marital status, level of education, etc.
- Behavioural data, collected by observing actions. Examples include clicks, time spent on a site or previous purchases.
- Geographical (or geolocalised) data provide information about physical location. This includes data such as location or IP address.
- Transactional data relates to purchases made (products purchased, frequency of purchase, average basket, etc.).
- Psychographic data concern interests, values, opinions and lifestyles. They go beyond demographics to capture consumer motivations and attitudes.
- Contextual data refers to information about the context of the interaction, such as the time of day, the location or the device used.
2. Different types of data depending on their source
But we also need to differentiate between data depending on how it is collected and its source. There are Zero-Party Data, First-Party Data, Second-Party Data and Third-Party Data.
1. Zero-Party Data
Zero-Party Data is information that consumers voluntarily share with the brand. This includes personal preferences, opinions, purchase intentions, wishes or specific feedback.
Advantages :
- User consent, which strengthens the trust between the brand and its audience;
- This data is invaluable for personalisation, as it reflects what users want or expect from a brand.
- Compliance with regulations (in particular the RGPD), as consumers have explicitly shared this information.
Disadvantages :
- They are difficult to collect because they depend on the goodwill of the consumer.
- There may be a bias in the responses if consumers are not honest or do not wish to share certain information.
2. First-Party Data
First-Party Data is data collected directly by the brand, through interactions with users on its channels (website, application, social networks, etc.). This includes information such as purchase history, browsing behaviour, account information, etc.
Advantages :
- This data is proprietary and therefore available to the brand.
- Collected directly, without the intermediary of third parties, which guarantees a certain reliability and protection of personal data.
- Easier to manage and analyse because the brand has total control.
Disadvantages :
- First-Party Data can be limited in quantity, as it depends on interactions with the brand.
- Large-scale collection is more difficult, particularly for brands with a small audience.
3. Second-Party Data
Second-Party Data is First-Party Data collected by another company. In other words, it is data collected by a partner and then shared ethically between the two parties.
Advantages :
- Allows brands to access data that they would not collect themselves, particularly if they do not have a very large customer base.
- Less intrusive than buying data from third parties (as in the case of Third-Party Data), because the data comes from partners with whom there is a relationship of trust.
Disadvantages :
- Limited availability, as you need to establish partnerships with other companies that share relevant data.
- The data may be less personalised than First-Party Data, because it comes from a different source.
4. Third-Party Data
Third-Party Data is data collected by third-party companies (other than the brand or its direct partners) and resold or shared with brands. These companies specialise in data collection and gather information about behaviour on different websites or across different platforms.
Advantages :
- Reaches new audiences that the brand would not otherwise have been able to identify.
- Can offer highly detailed data on user behaviour, consumer trends, etc.
Disadvantages :
- This data may be less accurate or reliable than First-Party Data, as it may lack context.
- Confidentiality issues: Using this data without users’ consent may entail legal risks (particularly with regulations such as the RGPD).
- Collecting this type of data can be perceived as intrusive, and some consumers use tools to avoid being tracked (e.g. ad blockers, VPNs).
To sum up, here is a summary infographic to help you remember the most important information:

Which data collection method should you choose?
Now that we have identified the types of data and the uses that companies can make of it, we turn our attention to data collection.The organisations have a range of tools
which can be used (in synergy) according to their objectives and needs. Here are the most effective.
1. CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
CRM software (Salesforce, Hubspot, Brevo) is used to collect, organise and analyse data throughout the buying process. These tools centralise the information collected on prospects and customers.
Use case :
- Enables First-Party data to be collected (contact information, purchase history, preferences, etc.).
- Helps personalise customer relations by centralising relevant information.
- Automate the collection and use of customer data by integrating other marketing tools (emailing, chatbot, etc.)
2. Gamification tools
Gamification consists of integrating game elements (interactive mechanics, challenges, rewards, etc.) into communication to encourage users to interact. Playable marketing attracts attention, stimulates engagement and collects data in a fun and less intrusive way than a form.
Use case :
- Game marketing boosts user engagement and encourages them to provide data (via a contact form before or after the game) in exchange for a stimulating experience and/or rewards.
- Certain mechanisms can make it easier to collect first-party data and identify needs and preferences. This is the case with Swiper or Battle, which identifies the specific interests or behaviour of each user.
- Surveys (or open quizzes) are gamified mechanisms for asking questions on a range of subjects (preferences, purchasing intentions, satisfaction, etc.).
- Gamification can be used to energise a loyalty programme to encourage redemption and provide the brand with accurate data.
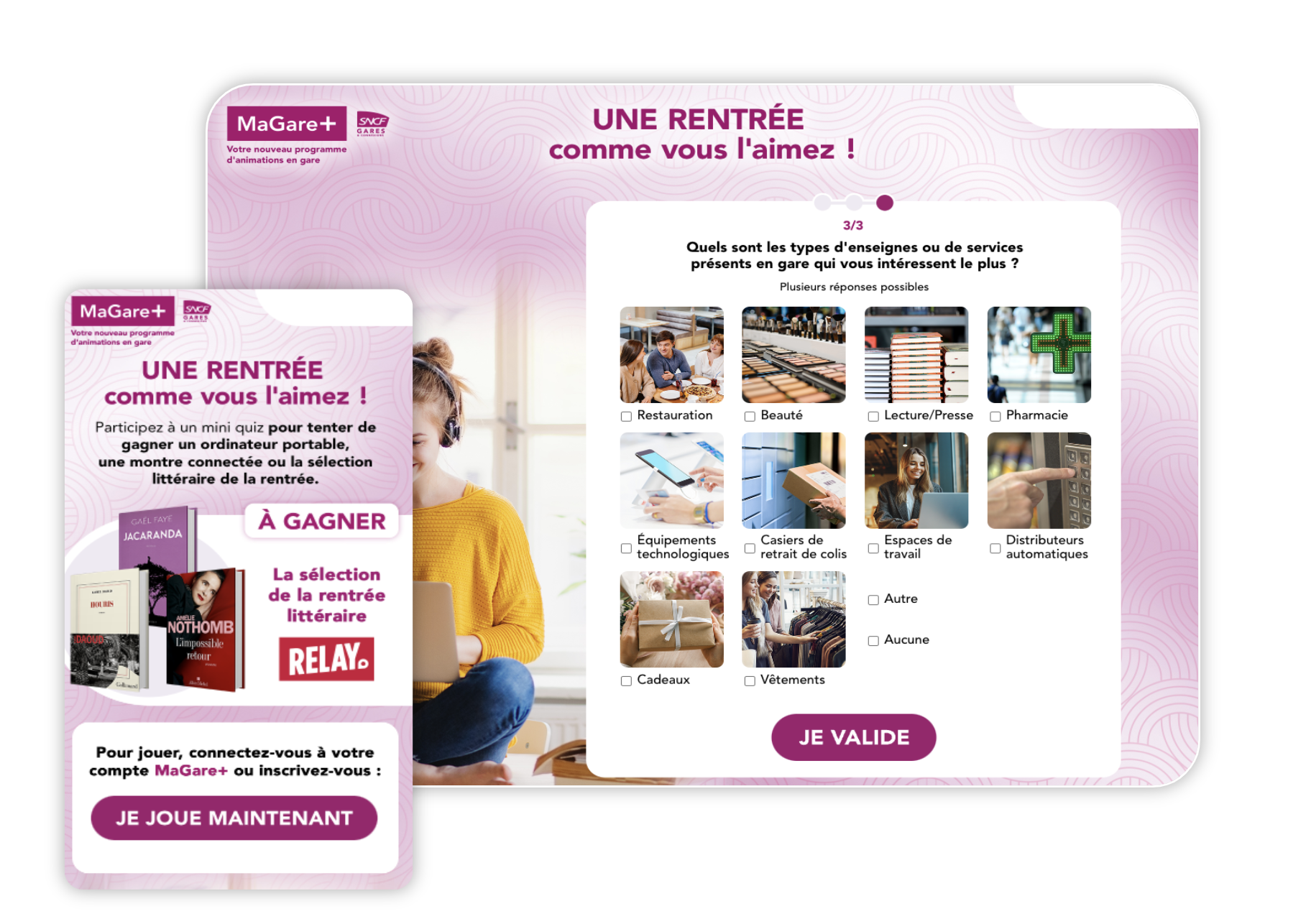
Ma Gare + ran a marketing competition, including a survey of travellers’ habits and their desire for station facilities. This quiz enabled Ma Gare + to collect more than 15,000 new qualified leads, many of which were new accounts.

3. Opt-in and data enrichment solutions
Opt-in collection solutions allow explicit consent to be collected (when subscribing to a newsletter or service). This type of collection makes it possible to enrich the data initially held on users, added to their profile from external sources.
Use case :
- Obtain explicit consent for data collection, thereby complying with regulations (e.g. RGPD).
- Collection of First-Party data to enrich profiles and understand their needs. When people sign up for a newsletter, they may indicate their interests or their location. This data is used to personalise communications according to preferences, by sending geolocated promotions.
4. Behavioural analysis tools
Behavioural analysis tools make it possible to track and analyse behaviour on a website or application (pages visited, time spent on each page, actions taken). These tools are invaluable for collecting behavioural data and understanding interactions with the brand.
Use case :
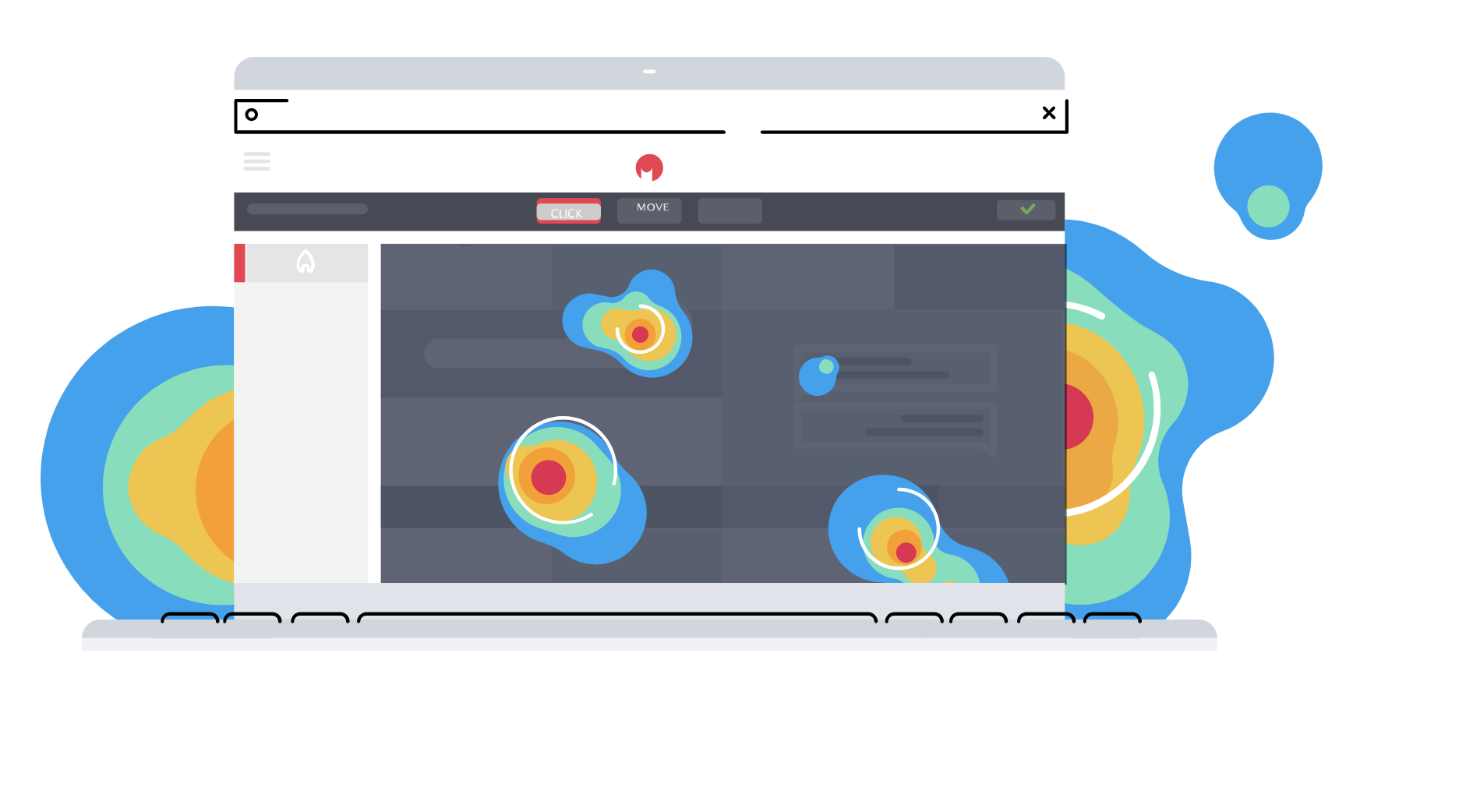
Tools such as Hotjar can be used to create heat maps to improve the design of the brand’s website or application. They help to understand which elements are noticed by users and which can be ignored. This helps designers to improve the interface by highlighting key elements.
In the same way, behavioural data can be collected by recording visitor sessions or analysing user engagement. This is also useful for optimising the user experience as well as conversion rates.
5. Tools for collecting data on social networks
Social network data collection tools allow you to retrieve information from interactions on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and so on. This includes behavioural, demographic and even psychographic data.
Use case :
- Provides access to a wealth of data on online behaviour.
- By tracking interactions and analysing data on social networks, we can understand their interests, opinions and attitudes, and therefore optimise content.
The choice of data collection tools therefore depends on the brand’s objectives, resources and the type of data it wishes to collect. It is advisable to combine these tools to obtain a complete picture of its audience while complying with the rules on consent and data protection.
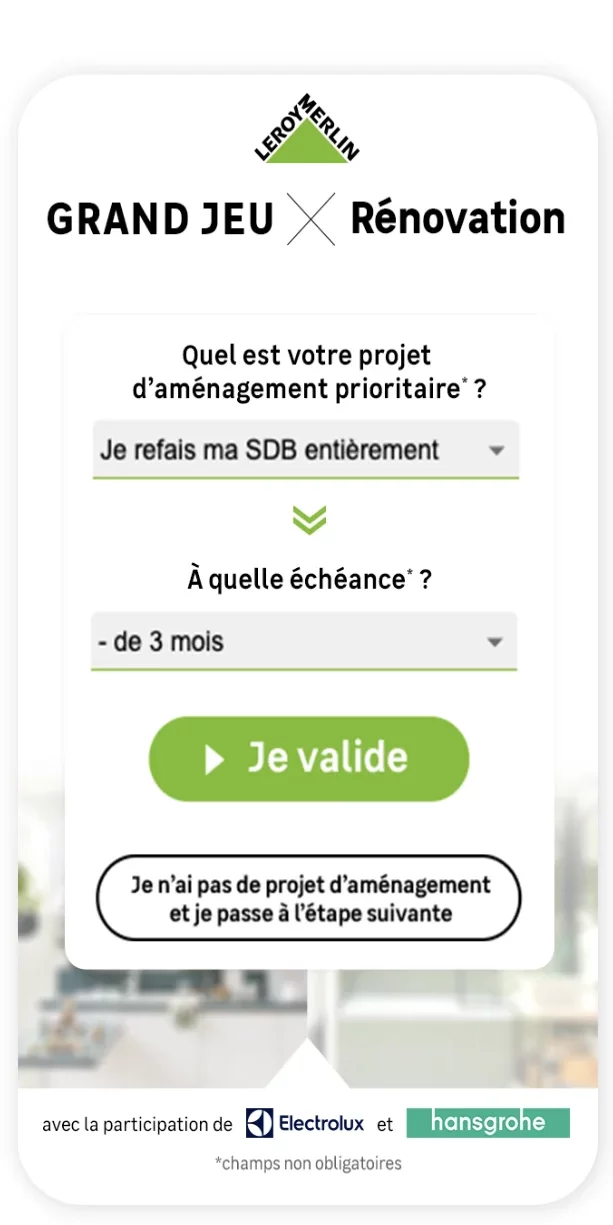
Customer data collection and Playable Marketing: the example of Leroy Merlin
Playable Marketing is one of the most effective methods of collecting data. By incorporating game elements into the collection process (quizzes, competitions, surveys), this lever offers a number of advantages:
- The collection of accurate data, shared by consumers ;
- Increased audience engagement through access to enriched information;
- Reducing friction in the collection process. Fun experiences to make it more enjoyable and less intrusive.
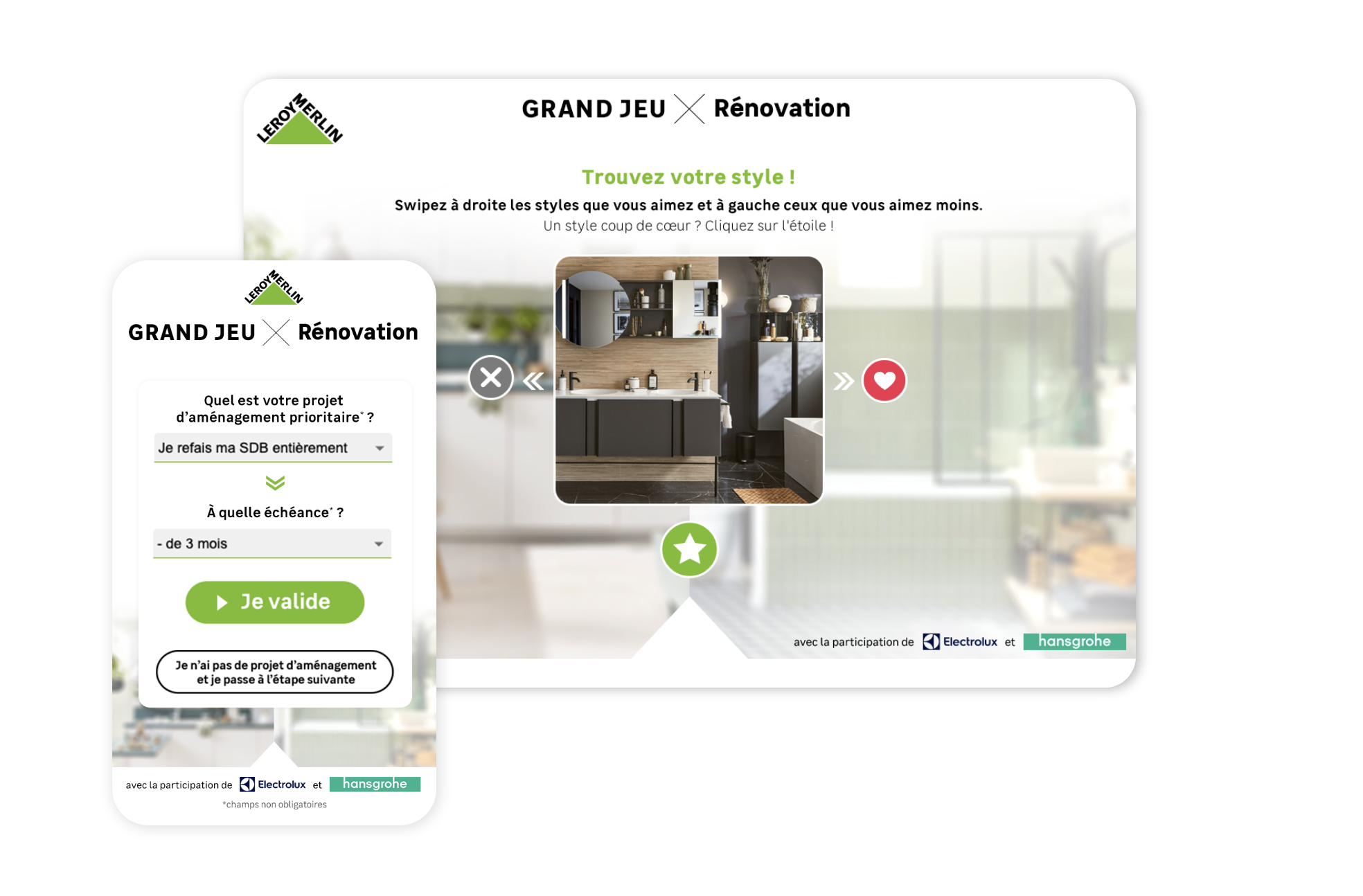
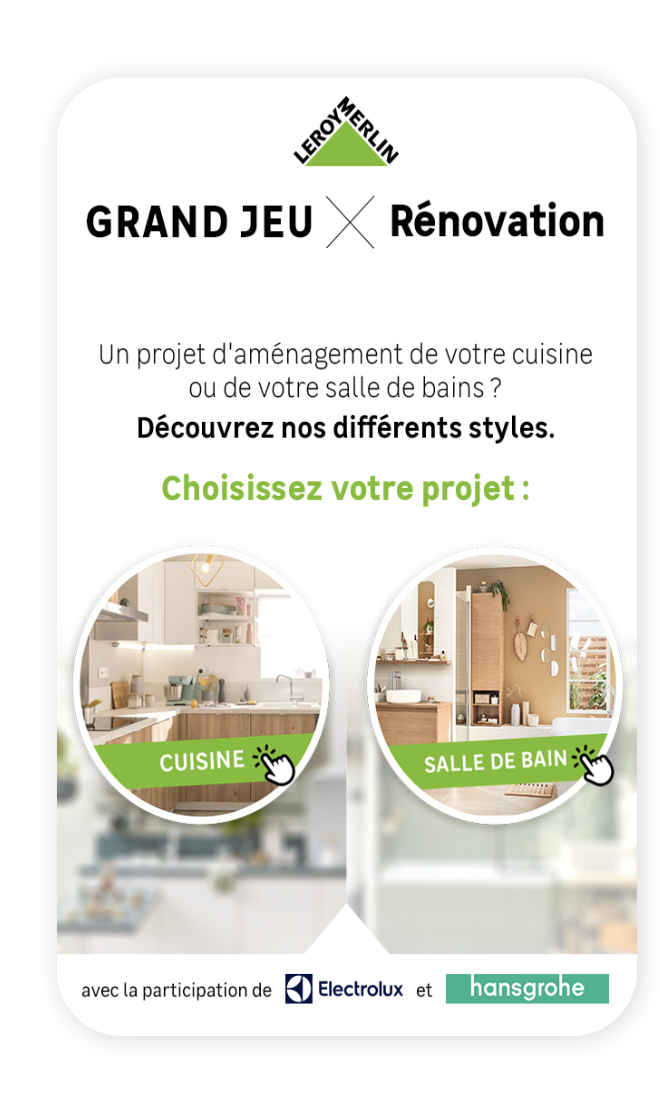
For these reasons, Leroy Merlin chose gamification to optimise its data collection strategy. The ‘Renovation’ campaign was based on a Swiper to identify its audience’s renovation projects.
This game enabled Leroy Merlin to collect leads (creation of customer accounts) and qualify them according to their preferences. Each lead was segmented according to its intentions and projects (kitchen, bathroom, decorating preferences), enabling the brand to send offers tailored to the needs of the participants.
The campaign has increased Leroy Merlin’s visibility and brand awareness. It inspired customers and prospects to launch renovation and home improvement projects. The campaign resulted in the collection of 3M pieces of information and increase traffic to the site with over 40k clicks.
Conclusion
Collecting data may seem like a complex subject, but there are a number of tools that can make the job easier, while improving the relationship and trust between your brand and your customers. Discover our interactive mechanisms and use gamification as a powerful lever for collecting qualified data!